
Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is one of the world’s most prevalent genetic diseases and the result of sickle-shaped deformations of the erythrocytes due to a genetic defect. People with Sickle Cell Disease frequently show steno-occlusive lesions in large cerebral arteries and microangiopathic lesions, causing ischemic stroke and silent infarcts that impact their neurocognitive development and quality of life. The disease is mainly found in areas with widespread cases of malaria and occurs from a gene mutation in the descendants of infected people. Through migration, Sickle Cell Anemia is spreading globally and has become a global public health issue.
TCD recommended as screening tool
Transcranial Doppler sonography (TCD) is the gold standard to assess blood flow velocities in the vessels of the Circle of Willis in SCD patients and predict the risk of stroke. TCD is highly recommended as a routine screening tool not only for Sickle Cell Disease diagnostics, but also for prognosis and for guiding therapy and treatment: exchange transfusions, hydroxyurea, allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant, recently approved drugs and new therapeutic options (gene therapy, gene editing).
DWL specific Sickle Cell Disease examination program
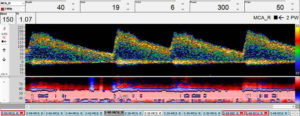
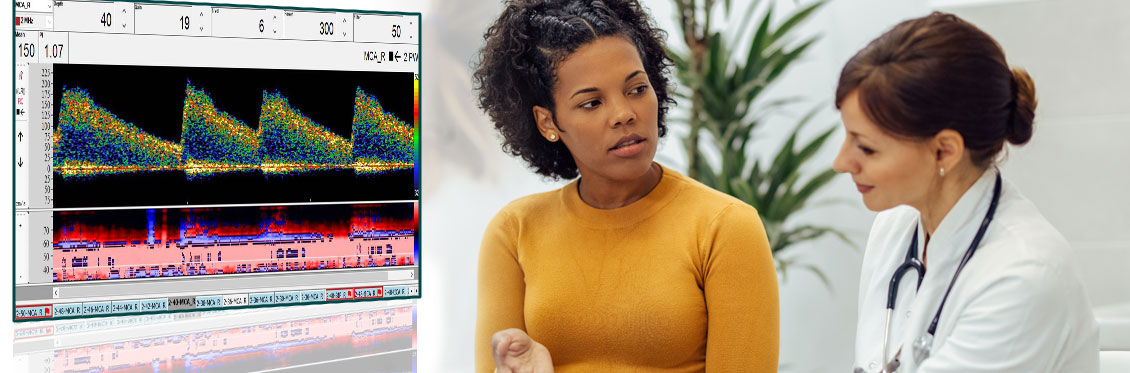
Sickle Cell Disease leads to occlusions of smaller and larger arteries with recurrent circulatory disturbances recognized by increased blood flow velocities. During an examination with the DWL routine program, the user is given the opportunity to automatically display the vessel sections with the highest blood flow velocities and therefore determines the relevant findings quickly and easily. The data obtained in this way can be made available in a report specially developed by DWL for faster diagnosis.
DWL specific SCD examination program includes:
- specific auto label list
- auto examination program – standard or customizable
- saving options of single spectra or prolonged recordings
- automatic identification of the segment with the highest mean velocity for each vessel and side
- marking of the recording (single spectra/prolonged recording) by a flag symbol
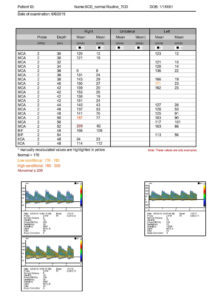
DWL specific SCD report includes:
- customizable SCD report in PDF format
- customizable target values for up to 4 different conditions (e.g., normal/low/high/abnormal)
- highlighted target values for fast identification of critical conditions
- automatic color marking of the target values
- options to include only highest mean values or selected recordings for simple assessment of critical conditions
- option to include spectrograms
- export option via DICOM and HL7
You can find more information about this in our Blog “The World of TCD Clinical Applications”.