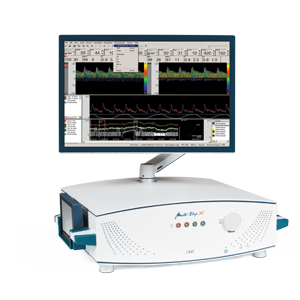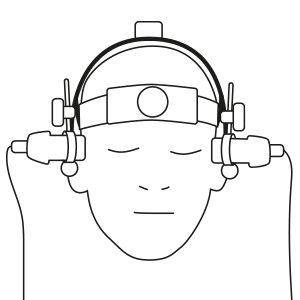
The TCD Waveform analysis software for cardiovascular physiology enables the differentiation of pathological and non-pathological findings with the aid of the Neuromon B.V. Doppler parameters and can be used, among other things, in surgery, anesthesia and intensive care.
The use of this innovative screening software allows physicians and healthcare professionals to quickly and reliably interpret the TCD signal in complex clinical situations, providing valuable information for further examinations.
For example:
- Age-related changes in the vascular flow area
- Changes in perfusion during therapeutic interventions, e.g. monitoring during medicinal treatment
- Pre-, peri- and postoperative examination (before / after evaluation)
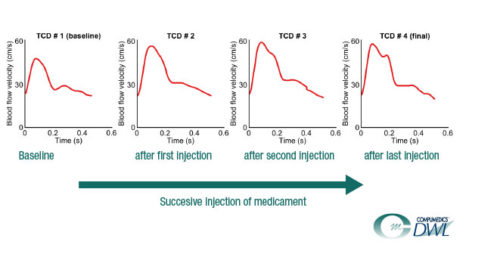
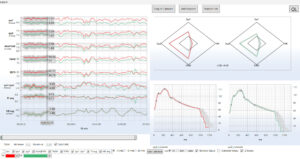
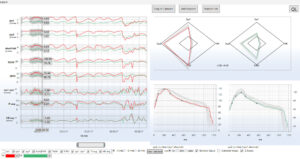
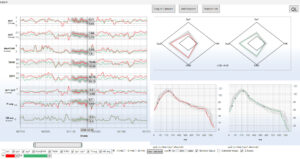
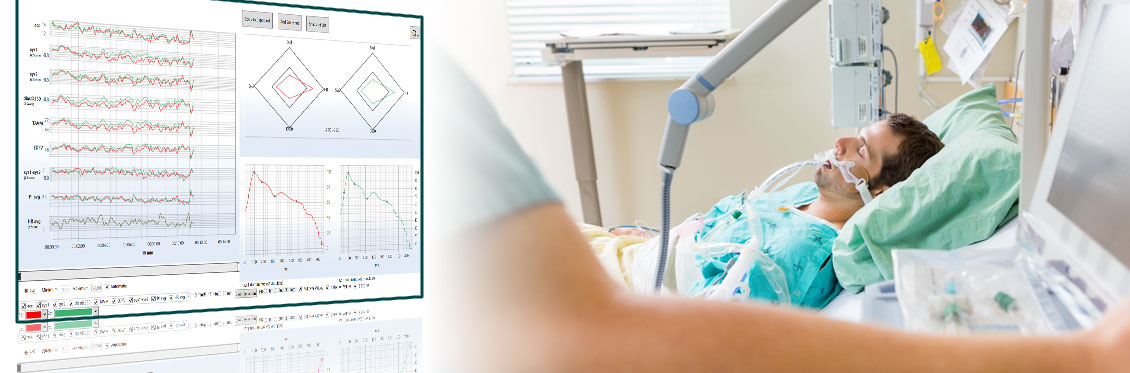
Patient with sepsis – therapy control medical treatment
Since the introduction of Transcranial Doppler Sonography (TCD) in the early 1980s, high expectations have been placed on using it as a tool for hemodynamic monitoring of the brain. Many studies have been performed to document changes in intracranial flow velocity under various conditions.
Quantitative analysis within these studies has been based on parameters defined at the onset of TCD: peak systole, end diastole, and average flow rate, from which quotients were calculated, e.g. the resistance index (RI) and the pulsatility index (PI).
The company Neuromon has further developed the existing TCD indexes for advanced TCD parameterization, whereupon appropriate software for the NMA module has been specially designed for DWL devices.
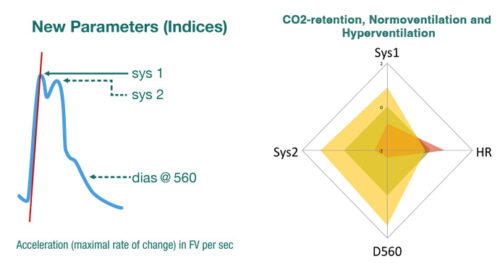
These advanced parameters are based on the theory of arterial acceleration, which states that the arterial vasculature is not just a passive conduit, but brings the energy into the pressure wave of the heart. This pressure wave is expanded within the smooth muscle cells of the arterial walls and spreads as a peristaltic wave along the branches of the Arterial Tree.
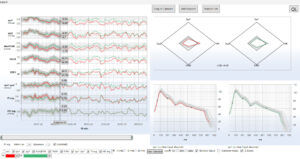
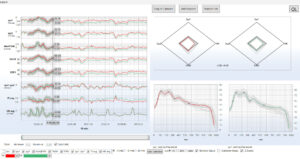
NMA incorporates Z-score analysis of middle cerebral artery flow velocity within. Z-score expresses how many standard deviations a given middle cerebral artery flow velocity measurement lies above or below the value expected for that age. Z-scores of different variables (Sys1, Sys2, D560 and HR) can be combined into a single radar plot to facilitate the rapid interpretation of intracranial hemodynamics in health and disease.
References
- Schaafsma, A. (2012). Improved Parameterization of the Transcranial Doppler Signal. Ultrasound in Medicine and Biology, 38(8), 1451-1459.
- Schaafsma A. Harvey with a modern twist: How and why conducting arteries amplify the pressurewave originating from the heart. Med Hypotheses. 2014;82(5):589-594.
- De Goede, A. A., Loef, B. G. Reidinga, A. C., & Schaafsma, A. (2017). Fluid Resuscitation in Septic Patients Improves Systolic but Not Diastolic Middle Cerebral Artery Flow Velocity, 43(11), 2591-2600.
In collaboration with
Illustrations exemplary. Findings depending on sex and age.