COVID-19 verursacht vermutlich Gefäßentzündung, Herzinfarkt, Schlaganfall
Es gibt vermehrt Forschungsergebnisse, die beschreiben, dass COVID-19 weniger eine Lungenerkrankung als eher eine systemische Gefäßerkrankung ist, die auch Schlaganfälle begünstigt. Demnach befällt der Coronavirus nicht nur die Atemwege, sondern auch das neurovaskuläre System das lebenswichtige Organe versorgt – Gehirn, Nieren und Lunge.
Bei Patienten, deren Gefäßfunktion durch Vorerkrankungen bereits beeinträchtigt ist, kann eine SARS-CoV-2-Infektion so besonders gefährlich werden. Somit lässt sich das typische Krankheitsbild erklären, indem es zu Zirkulationsstörungen am Herzen, sowie zu Lungenembolien und zu Gefäßverschlüssen im Gehirn und in den Nieren kommen kann. Diese können schließlich zu einem tödlichen Multiorganversagen führen. Die Wissenschaftler heben hervor, dass es vor allem multimorbide Patienten mit kardiovaskulären Risikofaktoren wie Bluthochdruck, hohe Blutfette (Hypercholesterinämie) und hohe Blutzuckerwerte (Diabetes mellitus) sind, die schwer an COVID-19 erkranken.
TCD zur Früherkennung und Therapiebestimmung
Mit Hilfe von TCD kann bei COVID-19 Patienten das Risiko für Gefäßerkrankungen erkannt und damit eine gezielte Entscheidung über deren Therapie und Behandlung getroffen werden.
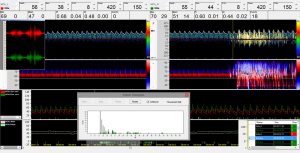
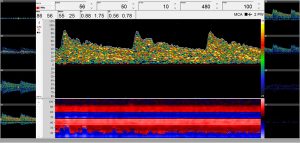
Verursacht der Coronavirus eine Gefäßentzündung (Vaskulitis), kommt es aufgrund der entzündlichen Reaktion zu einer Gefäßverengung mit relevanten Veränderungen der zerebralen Blutflussgeschwindigkeit (CBFV). Eine intrakraniellen Routine-Untersuchung kann bei der Diagnose von Vaskulitis helfen, indem es proximale zerebrale Gefäßanomalien verfolgt.
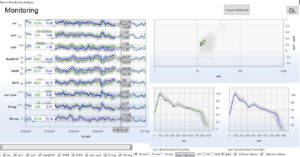
Die DWL Emboli Detektion Software sowie ein TCD-basierender PFO-Test können ein erhöhtes Risiko für Thrombosebildung und Schlaganfälle bei COVID-19-Patienten aufzeigen. So kann eine Therapie zur Behandlung effizienter und gezielter bestimmt werden.
Da eine Gefäßentzündung gravierenden Einfluss auf die Darstellung der Blutflusskurve hat, kann mittels der DWL Neuromonitoring Analyse (NMA) Software der Krankheits- und Therapieverlauf eines von COVID-19 betroffenen Patienten kontrolliert und optimiert werden.
Literatur
Vascular Events in COVID-19
The Spectrum of Neurologic Disease in the Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome Coronavirus 2 Pandemic Infection – Neurologists Move to the Frontlines; Samuel J. Pleasure, MD, PhD; Ari J. Green, MD; S. Andrew Josephson; JAMA Neurol. Published online April 10, 2020. DOI: 10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.1065 https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamaneurology/fullarticle/2764548; Department of Neurology and Weill Institute for Neuroscience, University of California, San Francisco.
Endothelial cell infection and endotheliitis in COVID-19; Zsuzsanna Varga; Andreas J Flammer; Peter Steiger; Martina Haberecker; Rea Andermatt; Annelies S. Zinkernagel et al. Published: April 20, 2020; DOI: 10.1016/S0140-6736(20)30937-5 https://www.thelancet.com/pdfs/journals/lancet/PIIS0140-6736(20)30937-5.pdf
Facing COVID-19 in the ICU: vascular dysfunction, thrombosis, and dysregulated inflammation; Safiya Richardson, MD, MPH1,2; Jamie S. Hirsch, MD, MA, MSB1,2,3; Mangala Narasimhan, Published online April 28, 2020. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs00134-020-06059-6
Incidence of thrombotic complications in critically ill ICU patients with COVID-19; F.A. Kloka, M.J.H.A. Kruipb, N.J.M. van der Meerc, M.S. Arbousd, D.A.M.P.J. Gommerse K.M. Kantf, F.H.J. Kapteina, J. van Paassend, M.A.M. Stalsa, M.V. Huismana,1, H. Endeman, DOI: 10.1016/j.thromres.2020.04.013 © 2020 Published by Elsevier Ltd https://www.thrombosisresearch.com/article/S0049-3848(20)30120-1/pdf
Acute ischemic stroke with COVID-19: an international consensus statement; Qureshi AI & al. Int J Stroke 03.05.2020 https://www.univadis.de/viewarticle/acute-ischemic-stroke-with-covid-19-an-international-consensus-statement-719799
COVID-19-Related Stroke; David C. Hess; Wael Eldahshan; Elizabeth Rutkowski; Translational Stroke Research; DOI: 10.1007/s12975-020-00818-9; 06.05.2020 https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12975-020-00818-9
Blood Clots & Strokes in COVID-19; ACE-2 Receptor; Oxidative Stress
Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area; Safiya Richardson, MD, MPH; Jamie S. Hirsch, MD, MA, MSB; Mangala Narasimhan, DO; JAMA. Published online April 22, 2020. DOI:10.1001/jama.2020.6775; https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2765184
Severe COVID-19 infection associated with endothelial activation; Robert Eschera, Neal Breakeya, Bernhard Lämmle; Letter to the Editors-in-Chief|
Volume 190, P62, June 01, 2020
Angiotensin converting enzyme-2 confers endothelial protection and attenuates atherosclerosis; Lovren F, Pan Y, Quan A, Teoh H, Wang G, Shukla PC, Levitt KS, Oudit GY, Al-Omran M, Stewart DJ, Slutsky AS, Peterson MD, Backx PH, Penninger JM, Verma S., Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 Oct;295(4):H1377-84. DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00331.2008. Epub 2008 Jul 25.
COVID-19 and Oxidative Stress (Prevention & Risk Factors)
Immune responses in COVID-19 and potential vaccines: Lessons learned from SARS and MERS epidemic; Eakachai Prompetchara, Chutitorn Ketloy, Tanapat Palaga; Asian Pac J Allergy Immunol 2020;38:1-9 DOI: 10.12932/AP-200220-0772; https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/ajpheart.00331.2008
Angiotensin converting enzyme-2 confers endothelial protection and attenuates atherosclerosis; Lovren F, Pan Y, Quan A, Teoh H, Wang G, Shukla PC, Levitt KS, Oudit GY, Al-Omran M, Stewart DJ, Slutsky AS, Peterson MD, Backx PH, Penninger JM, Verma S., Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 Oct;295(4):H1377-84. DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00331.2008. Epub 2008 Jul 25. https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/ajpheart.00331.2008
ACE2 and Ang-(1–7) protect endothelial cell function and prevent early atherosclerosis by inhibiting inflammatory response;
Zhang YH, Zhang YH, Dong XF, Hao QQ, Zhou XM, Yu QT, Li SY, Chen X, Tengbeh AF, Dong B, Zhang Y.; Inflamm Res. 2015 Apr;64(3-4):253-60. DOI: 10.1007/s00011-015-0805-1 Epub 2015 Feb 27; Department of Cardiology, Shandong Provincial Hospital Affiliated to Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong, China.
Local angiotensin-(1-7) administration improves microvascular endothelial function in women who have had preeclampsia. Stanhewicz AE, Alexander LM; Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2020 Jan 1;318(1):R148-R155. DOI: 10.1152/ajpregu.00221.2019. Epub 2019 Oct 2 Noll Laboratory, Department of Kinesiology, The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, Pennsylvania. https://pennstate.pure.elsevier.com/en/publications/local-angiotensin-17-administration-improves-microvascular-endoth
Presenting Characteristics, Comorbidities, and Outcomes Among 5700 Patients Hospitalized With COVID-19 in the New York City Area; Safiya Richardson, MD, MPH; Jamie S. Hirsch, MD, MA, MSB; Mangala Narasimhan, DO; JAMA. Published online April 22, 2020. DOI:10.1001/jama.2020.6775; https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/2765184
Nutrients and Oxidative Stress: Friend or Foe? Bee Ling Tan,Mohd Esa Norhaizan and Winnie-Pui-Pui LiewOxidative Medicine and Cellular LongevityVolume 2018, Article ID 9719584, 24 pages; DOI: 10.1155/2018/9719584; https://www.researchgate.net/publication/322852493_Nutrients_and_Oxidative_Stress_Friend_or_Foe
Oxidative stress in endothelial cell dysfunction and thrombosis; Joseph Loscalzo, M.D., Ph.D.; Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb 2002;32:359–360; DOI: 10.1159/000073600;
Angiotensin converting enzyme-2 confers endothelial protection and attenuates atherosclerosis; Lovren F1, Pan Y, Quan A, Teoh H, Wang G, Shukla PC, Levitt KS, Oudit GY, Al-Omran M, Stewart DJ, Slutsky AS, Peterson MD, Backx PH, Penninger JM, Verma S., Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 2008 Oct;295(4): H1377-84. DOI: 10.1152/ajpheart.00331.2008. Epub 2008 Jul 25.; https://journals.physiology.org/doi/full/10.1152/ajpheart.00331.2008
Quellen
Prof. F. Ruschitzka, Direktor der Kardiologie an der Zürcher Klinik
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lancet/article/PIIS0140-6736(20)30937-5/fulltext
Prof. Dr. Götz Thomalla, Hamburg, Sprecher der DGN-Kommission Zerebrovaskuläre Erkrankungen Prof. Peter Berlit, Generalsekretär der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Neurologie (DGN))
https://www.mta-dialog.de/artikel/ist-sars-cov-2-ein-schlaganfallausloeser.html
Prof. Klaus Püschel, Direktor am Institut für Rechtsmedizin des Universitätsklinikums Hamburg-Eppendorf (UKE)
https://www.acpjournals.org/aim/fullarticle/2765934/autopsy-findings-venous-thromboembolism-patients-covid-19-prospective-cohort-study
Wichmann D et al. Autopsy findings and venous thromboembolism in patients with COVID-19: a prospective cohort study. Ann Intern Med. 06.05.2020
Roger D. Seheult, MD, Pulmologe, Banning Specialty Care Center, California, USA
Coronavirus Pandemic Update 61: Blood Clots & Strokes in COVID-19; ACE-2 Receptor; Oxidative Stress https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=22Bn8jsGI54
Coronavirus Pandemic Update 65: COVID-19 and Oxidative Stress (Prevention & Risk Factors) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gzx8LH4Fjic
Neurologic Manifestations of Hospitalized Patients With Coronavirus Disease 2019 in Wuhan, China Ling Mao; Huijuan Jin; Mengdie Wang; et al Yu Hu; Shengcai Chen; Quanwei He; Jiang Chang; Candong Hong; Yifan Zhou; David Wang; Xiaoping Miao; Yanan Li, MD, PhD; Bo Hu, MD, PhD JAMA Neurol. published online April 10, 2020. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.1127 JAMA Neurol. published online April 10, 2020. doi:10.1001/jamaneurol.2020.1127
Abbildungen beispielhaft. Befundungen abhängig von Geschlecht und Alter.